Atrial Fibrillation
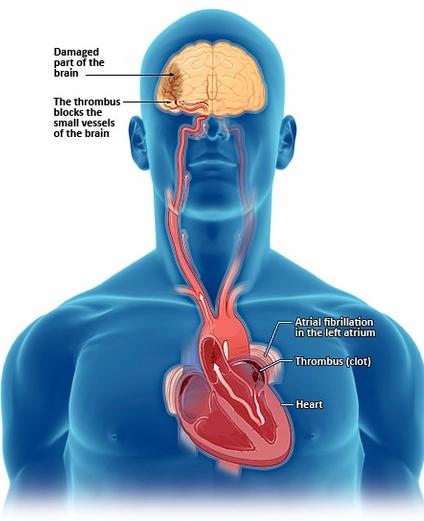
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is an unpredictable heart rhythm disorder that can cause unsettling symptoms like rapid heartbeats, fatigue, and dizziness. Naturally, if you’re dealing with this, the first question that probably comes to mind is: “Does AFib ever go away?”
The simple answer is that AFib doesn’t typically go away on its own. It’s a chronic condition, but the good news is that, with the right treatment and lifestyle modifications, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of AFib episodes. Some patients might go months—or even years—without any symptoms. Let’s break down what this means for you.
Understanding AFib: The Basics
Before we dive into whether AFib can disappear, let’s quickly recap what it is. In people with AFib, the heart’s upper chambers (the atria) beat irregularly, leading to inefficient blood flow. This can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe complications like stroke.
AFib can occur sporadically (known as paroxysmal AFib) or be more persistent. In the persistent form, the episodes don’t stop on their own and often require medical intervention.
So, Can AFib Go Away on Its Own?
Let’s get straight to the point: for the majority of people, AFib won’t simply vanish forever. AFib is a condition that tends to evolve over time. Even if your heart rhythm returns to normal for periods, it doesn’t mean the AFib is gone for good.
“AFib doesn’t usually go away,” I often tell my patients, especially when they’re initially diagnosed. “It’s something we manage, not something that magically disappears.”
For patients with paroxysmal AFib, episodes may come and go unpredictably, but without ongoing treatment or lifestyle changes, they can become more frequent. Persistent AFib, on the other hand, often sticks around until more aggressive intervention—like cardioversion, medication, or ablation—is used to restore normal rhythm.
Why Doesn’t AFib Go Away?
The underlying causes of AFib typically don’t resolve by themselves. For many, it’s tied to age, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, or other underlying health conditions. As time goes on, these factors may worsen, making AFib more difficult to control. Left unchecked, AFib can progress from short, sporadic episodes to a permanent condition.
The Role of Lifestyle Modifications
While AFib itself doesn’t typically disappear, certain lifestyle changes can dramatically improve how often you experience AFib and how intense the symptoms are. In fact, lifestyle modification can change the course of AFib by reducing the number of spells, slowing disease progression, and increasing the chances of successful treatment.
Weight Loss: One of the most important lifestyle modifications is managing weight. Studies show that weight loss in overweight or obese patients with AFib can reduce episodes and even improve the success rate of treatments like ablation. Keeping a healthy weight can help lower blood pressure, improve heart function, and reduce the burden of AFib.
Exercise: Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in heart health. I’m not talking about extreme marathon training here, but rather, incorporating moderate exercise into your routine, such as walking, swimming, or cycling. However, make sure to discuss your exercise plans with your doctor, as not all forms of exercise may be appropriate for every AFib patient.
Diet: A heart-healthy diet, rich in vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help manage conditions like high blood pressure and cholesterol that contribute to AFib. Limiting salt, avoiding excessive alcohol, and reducing caffeine can also lessen the frequency of AFib episodes.
Sleep Apnea Treatment: If you have sleep apnea, treating it can significantly reduce your AFib burden. Sleep apnea puts extra strain on your heart and is a major trigger for AFib.
Can Treatment Make AFib Disappear?
While AFib is not typically “curable” in the traditional sense, there are treatments that can help you manage and reduce episodes—sometimes even making it feel like the condition has gone away. However, it’s crucial to remember that managing AFib is an ongoing process.
1. Medications
AFib medications fall into two main categories: rhythm control and rate control.
- Rhythm control medications aim to restore your heart’s normal rhythm. These drugs can help, especially early in the disease’s progression. However, most patients will have recurrences.
- Rate control medications don’t fix the irregular rhythm but help slow down your heart rate to reduce symptoms.
Both approaches can improve your quality of life, but they rarely make AFib disappear altogether.
2. Cardioversion
Cardioversion is a procedure that uses electrical shocks or medications to reset your heart’s rhythm. While it can restore a normal rhythm in the short term, AFib often returns without ongoing treatment or lifestyle changes.
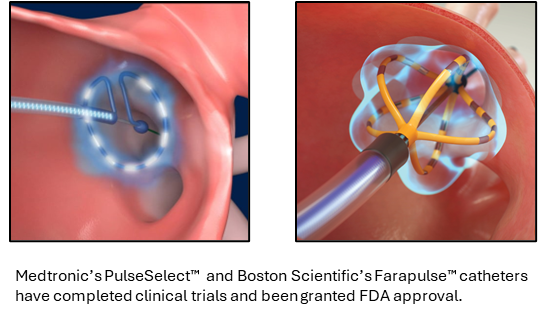
3. Ablation
For many of my patients, catheter ablation has been a game-changer. This minimally invasive procedure uses heat or cold energy to create small scars in the heart tissue, which disrupts the abnormal electrical signals causing AFib.
Ablation can significantly reduce the number of AFib episodes, and in some cases, patients might go years without any symptoms. However, even after ablation, AFib can still return. The success of the procedure depends on factors like how long you’ve had AFib and whether you’ve made those crucial lifestyle changes.
“Ablation doesn’t make AFib disappear for everyone, but it’s an important tool in reducing its impact on your life,” I often tell my patients, especially those looking for long-term solutions.
4. Lifestyle Modifications Post-Treatment
Lifestyle changes remain critical, even after procedures like ablation or cardioversion. Without a healthy lifestyle, the benefits of treatment may be short-lived. As I always say, the best approach to managing AFib is a holistic one—combining the right treatment with healthy living.
Managing AFib Long-Term: What Can You Do?
While AFib doesn’t typically go away, it’s not a life sentence to constant symptoms or reduced quality of life. The key is finding the right treatment strategy that works for you and sticking to a healthy lifestyle that supports your heart.
Tracking Progress: Keep an eye on your symptoms. If you’re noticing more frequent episodes, consult with your doctor. Together, you can adjust your treatment plan and lifestyle to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Monitoring Triggers: Everyone’s AFib triggers are different. Stress, poor sleep, alcohol, and caffeine are common culprits. By tracking what sets off your episodes, you can avoid or minimize those triggers.
Conclusion: Living Well with AFib
So, can AFib go away? Not typically. But that doesn’t mean it has to control your life. With the right combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, many people with AFib live active, fulfilling lives.
If you’re dealing with AFib, you’re not alone. At The AFib Clinic, we specialize in providing comprehensive care for patients with atrial fibrillation. We work closely with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses both the medical and lifestyle aspects of AFib. Whether you’re considering catheter ablation or need guidance on lifestyle modifications, we’re here to help every step of the way.
For more information, feel free to explore our treatment options. And remember, AFib may not disappear, but together, we can manage it effectively.
Dr Jose Osorio
Miami, FL
Read more about AFib:
Can Weight Loss Drugs Like Wegovy, Mounjaro and Zepbound Help Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)?
Improving Success Rates for Afib Ablation by Building a Learning Collaborative – Dr Jose Osorio
What are the success rates of Afib Ablation? How do physicians know the chances of success?